Funzione MySQL CONCAT()
Ultimo aggiornamento del 26 febbraio 2020 08:08:24 (UTC/GMT +8 ore)
Funzione CONCAT()
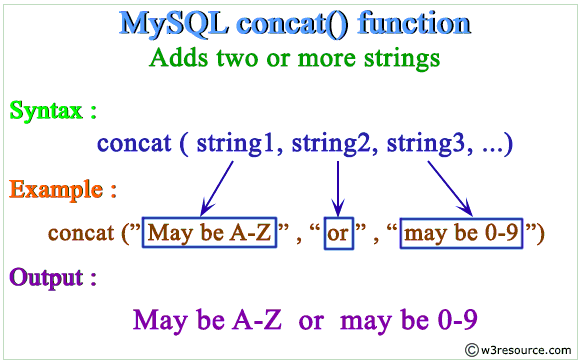
La funzione MySQL CONCAT() è usata per aggiungere due o più stringhe.
- Ci possono essere uno o più argomenti.
- Ritorna la stringa che risulta dalla concatenazione degli argomenti.
- Ritorna una stringa non binaria, se tutti gli argomenti sono stringhe non binarie.
- Ritorna una stringa binaria, se gli argomenti includono qualsiasi stringa binaria.
- Se l’argomento è numerico, viene convertito nella sua forma equivalente di stringa non binaria.
- Ritorna NULL se qualsiasi argomento è NULL.
Sintassi:
CONCAT (string1, string2,…)
Argomenti
| Nome | Descrizione |
|---|---|
| stringa1 | Prima stringa da unire. |
| stringa2 | Seconda stringa da unire. Fino a un numero N di stringhe può essere specificato in questo modo. |
Diagramma sintattico:
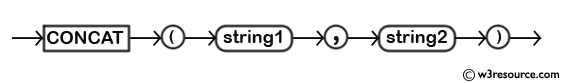
MySQL Versione: 5.6
Rappresentazione pittografica della funzione MySQL CONCAT()
Presentazione video
Il tuo browser non supporta il video HTML5.
Esempio della funzione MySQL Concat utilizzando gli argomenti
Un argomento:
mysql> SELECT CONCAT('w3resource');+----------------------+| CONCAT('w3resource') |+----------------------+| w3resource |+----------------------+1 row in set (0.00 sec)
Due o più argomenti:
mysql> SELECT CONCAT('w3resource','.','com');+--------------------------------+| CONCAT('w3resource','.','com') |+--------------------------------+| w3resource.com |+--------------------------------+1 row in set (0.00 sec)
Uno degli argomenti è NULL :
mysql> SELECT CONCAT('w3resource','.','com',NULL);+-------------------------------------+| CONCAT('w3resource','.','com',NULL) |+-------------------------------------+| NULL |+-------------------------------------+1 row in set (0.02 sec)
Argomento numerico:
mysql> SELECT CONCAT(102.33);+----------------+| CONCAT(102.33) |+----------------+| 102.33 |+----------------+1 row in set (0.00 sec)
Per le stringhe quotate, la concatenazione può essere eseguita mettendo le stringhe una accanto all’altra:
mysql> SELECT 'w3resource' '.' 'com';+----------------+| w3resource |+----------------+| w3resource.com | +----------------+1 row in set (0.00 sec)
Esempio della funzione MySQL CONCAT() sulle colonne
La seguente istruzione MySQL aggiungerà i valori della colonna pub_city con i valori della colonna country della tabella publisher mettendo un ‘–>’ tra loro.
Codice:
SELECT CONCAT(pub_city,'--> ',country)FROM publisher; Tabella campione: publisher
Esito campione:
mysql> SELECT CONCAT(pub_city,'--> ',country) -> FROM publisher;+---------------------------------+| CONCAT(pub_city,'--> ',country) |+---------------------------------+| New York--> USA | | Mumbai--> India | | Adelaide--> Australia | | London--> UK | | Houstan--> USA | | New York--> USA | | Cambridge--> UK | | New Delhi--> India | +---------------------------------+8 rows in set (0.00 sec)
MySQL CONCAT usando la clausola WHERE
La seguente istruzione MySQL aggiungerà la colonna pub_city e country con un ‘–>’ per quegli editori il cui nome concatenato e la sede del paese è ‘Ultra Press Inc. London’
Codice:
SELECT CONCAT(pub_city,'--> ',country)FROM publisherWHERE CONCAT(pub_name,' ',country_office)="Ultra Press Inc. London"; Tabella campione: editore
Esito campione:
mysql> SELECT CONCAT(pub_city,'--> ',country) -> FROM publisher -> WHERE CONCAT(pub_name,' ',country_office)="Ultra Press Inc. London";+---------------------------------+| CONCAT(pub_city,'--> ',country) |+---------------------------------+| London--> UK |+---------------------------------+1 row in set (0.02 sec)
MySQL CONCAT restituisce NULL se qualsiasi campo contiene NULL
La seguente istruzione MySQL aggiungerà il nome del libro e la colonna pub_lang con un ‘–>’ per tutti i libri.
Codice:
SELECT CONCAT(book_name,'--> ',pub_lang)FROM book_mast;Tabella d’esempio: book_mast
Esito campione:
mysql> SELECT CONCAT(book_name,'--> ',pub_lang) -> FROM book_mast;+------------------------------------------------+| CONCAT(book_name,'--> ',pub_lang) |+------------------------------------------------+| Introduction to Electrodynamics--> English || Understanding of Steel Construction--> English || Guide to Networking--> Hindi || Transfer of Heat and Mass--> English || NULL || Fundamentals of Heat--> German || Advanced 3d Graphics--> Hindi || Human Anatomy--> German || Mental Health Nursing--> English || Fundamentals of Thermodynamics--> English || The Experimental Analysis of Cat--> French || The Nature of World--> English || Environment a Sustainable Future--> German || NULL || Anatomy & Physiology--> Hindi || Networks and Telecommunications--> French |+------------------------------------------------+16 rows in set (0.01 sec)
L’output di cui sopra mostra che, quando il valore di una delle due colonne menzionate sopra è NULL, l’output restituisce NULL, menzionato dal colore rosso.
MySQL CONCAT usando JOINS e caratteri jolly
La seguente istruzione MySQL mostrerà la combinazione di nome, cognome e titolo di lavoro per quegli impiegati che contengono la parola Smith nella loro combinazione di nome e cognome.
Codice:
SELECT CONCAT( first_name, ' ', last_name ) AS "name", job_titleFROM employees e, jobs jWHERE e.job_id = j.job_idAND CONCAT( first_name, ' ', last_name ) LIKE '%Smith%';Tabella campione: dipendenti
Tabella campione: lavori
Uscita campione:
mysql> SELECT CONCAT( first_name, ' ', last_name ) AS "name", job_title -> FROM employees e, jobs j -> WHERE e.job_id = j.job_id -> AND CONCAT( first_name, ' ', last_name ) LIKE '%Smith%';+---------------+----------------------+| name | job_title |+---------------+----------------------+| Lindsey Smith | Sales Representative || William Smith | Sales Representative |+---------------+----------------------+2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
PHPScript
<!doctype html><html lang="en"><head><meta charset="utf-8"><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1"><title>example-concat-function - php mysql examples | w3resource</title><meta name="description" content="example-concat-function - php mysql examples | w3resource"><link rel="stylesheet" href="https://maxcdn.bootstrapcdn.com/bootstrap/3.3.5/css/bootstrap.min.css"></head><body><div class="container"><div class="row"><div class="col-md-12"><h2>list of publisher's city and country with 'publisher's city--->country' format:</h2><table class='table table-bordered'><tr><th>Publisher's City</th></tr><?php$hostname="your_hostname";$username="your_username";$password="your_password";$db = "your_dbname";$dbh = new PDO("mysql:host=$hostname;dbname=$db", $username, $password);foreach($dbh->query('SELECT CONCAT(pub_city,"--> ",country)FROM publisher') as $row) {echo "<tr>";echo "<td>" . $row . "</td>";echo "</tr>";}?></tbody></table></div></div></div></body></html>JSPScript
<%@page contentType="text/html" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%><%@ page import="java.sql.*" %><%@ page import="java.io.*" %><!DOCTYPE html><html><head><meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8"><title>example-concat-function</title></head><body><%try {Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver").newInstance();String Host = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/w3resour_bookinfo";Connection connection = null;Statement statement = null;ResultSet rs = null;connection = DriverManager.getConnection(Host, "root", "datasoft123");statement = connection.createStatement();String Data ="SELECT CONCAT(pub_city,'--> ',country) FROM publisher";rs = statement.executeQuery(Data);%><TABLE border="1"><tr width="10" bgcolor="#9979"><td>Publisher's City</td></tr><%while (rs.next()) {%><TR><TD><%=rs.getString("CONCAT(pub_city,'--> ',country)")%></TD></TR><% } %></table><%rs.close();statement.close();connection.close();} catch (Exception ex) {out.println("Cant connect to database.");}%></body></html>Prova le seguenti query
Scrivere una dichiarazione SQL per visualizzare la città e il nome dell’editore in base al gruppo sulla città dell’editore.
Scrivi un comando SQL per visualizzare la città e il nome dell’editore e l’ufficio nazionale con un titolo adatto per quegli editori che hanno l’ufficio nazionale e la città dell’editore nello stesso posto.
Scrivi un comando SQL per visualizzare il nome dell’editore, l’ufficio nazionale e il numero massimo di filiali con il titolo adatto per quegli editori che mantengono più di 15 filiali nel mondo.
Tabella d’esempio: editore
MySQL Online Editor
Visualizza risposta
SELECT CONCAT(‘City:- ‘,pub_city,’ Nome editore :- ‘,pub_name,’ Ufficio paese :- ‘,country_office)
FROM publisher
WHERE pub_city=country_office
GROUP BY pub_city;
SELECT CONCAT(‘Publisher Name :- ‘,pub_name,
‘Country Office:- ‘,country_office,
‘Numero massimo di filiali:- ‘,Max(no_of_branch))
FROM publisher
GROUP BY pub_name
HAVING Max(no_of_branch)>=15;